Think back to your high school chemistry class for a moment. Do you remember what salt is? If you said sodium chloride, you’re correct.
Now can you think of a few of the key electrolytes? If your answer included sodium and chloride, again, you’re correct, A+.
Sodium chloride, what we know as salt, is composed of a combination of two electrolyte minerals. While it may not seem like the most obvious concept, we need salt to maintain optimal hydration levels, as well as optimal electrolyte levels. Not sure how this all works? In this article, we’ll dive into why we need salt for hydration and how to choose the best salt for electrolytes to hydrate our bodies naturally.
Table of Contents
Short Summary
- Electrolytes are electrically charged minerals that are key for hydration and other important functions within our bodies.
- Salt mainly consists of sodium and chloride, while some variations contain trace minerals as well.
- Salt can be used to help replenish electrolytes and rehydrate your body.
What Are Electrolytes?
Let’s start with the basics: electrolytes are electrically charged minerals that are found in our bodies.
Key electrolytes include:
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Phosphorus
- Calcium
- Chloride
- Magnesium
We get essential electrolytes from food, beverages, and some supplements.
The Importance of Electrolytes
Electrolytes play a key role in many functions within our bodies. A few of these include:
- Balancing our hydration status
- Balancing our fluid balance, including levels both inside and between our cells
- Maintaining our body’s pH level
- Facilitating muscle contraction and other nerve and muscle function
The Problem of Electrolyte Imbalance
As with all things, our body continually strives for electrolyte balance. However, it isn’t always possible. Electrolyte imbalance occurs when we have an oversupply of some electrolytes and/or an undersupply of others. An oversupply or undersupply of fluid in our bodies is also associated with electrolyte imbalance.
Electrolyte imbalances are most often triggered by sweating out large amounts of fluid and electrolytes or vomiting and/or diarrhea. Other causes of electrolyte imbalances include some chronic diseases, such as chronic kidney disease, and the use of certain medications.

Benefits of Adding Electrolytes to Water
You may hear of athletes adding electrolytes to their water. Many electrolyte beverages are available today. These beverages range from classic sports drinks like Gatorade and Powerade to electrolyte powders like Liquid IV and LMNT or electrolyte tablets like Nuun. Electrolytes are also naturally found in beverages like coconut water and foods like bananas and yogurt.
But why add electrolytes to your water? Electrolytes can improve hydration by replenishing any lost minerals and allowing your body to rehydrate efficiently and effectively.
Importance of Sodium for Athletes
As an athlete, you are likely training at a high intensity very frequently. You’re also likely sweating a ton. When we sweat, we lose electrolytes and fluid, including sodium. In order to totally replenish our bodies, we need to replace both the fluid we lost, as well as the electrolytes.
While the average, sedentary person may want to cut back on sodium for optimal health, athletes lose sodium often and need to focus on replacing it to maintain both proper hydration and health.
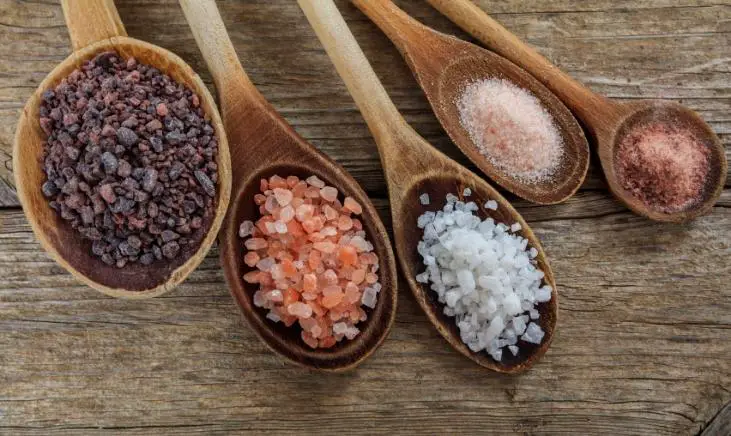
What Type of Salt is Best for Hydration?
Salt is not just salt. In fact, there are many different variations of salt and types of processed salt. Let’s dive into a few.
Table Salt
Table salt is generally made up of sodium, chloride, and some additives to prevent it from clumping. It is often iodized salt, meaning iodine is added to it to prevent iodine deficiency in the general population.
Table salt contains 2300 milligrams of sodium per teaspoon.

Kosher Salt
Kosher salt, like regular table salt, is composed of only sodium and chloride; it contains no other minerals. However, it is free of additives.
Kosher salt contains 1920 milligrams of sodium per teaspoon.
Sea Salt
Sea salt contains sodium, chloride, and other trace amounts of minerals including iron, potassium, magnesium, and zinc.
Celtic sea salts are a specific variation of sea salt that have a slightly different mineral composition than other sea salts.
The sodium content of sea salts vary based on how they are ground. Finely ground sea salt contains 2120 milligrams of sodium per teaspoon, while coarsest ground sea salt contains 1560 milligrams of sodium per teaspoon.

Himalayan Pink Salt
Pink Himalayan salt also contains sodium, chloride, and other trace minerals including iron, potassium, and magnesium.
Pink Himalayan salt contains 2200 milligrams of sodium per teaspoon.
Salt Tablets
Salt tablets are sometimes used by athletes as a quick, easy way to replenish salt. The composition of salt tablets varies by brand with some containing a combination of other electrolytes, minerals, and even vitamins.
The amount of sodium also varies by tablet.
What is the Best Salt for Electrolytes?
You may think because sea salt and Himalayan pink salt contain potassium and magnesium, in addition to sodium and chloride, they are better choices for replenishing electrolytes. However, from a nutrition standpoint, there isn’t a real difference in the rehydration capabilities of these variations of salt. While the mineral composition does vary, the quantities of these other minerals are not large enough to make a significant impact.
Can I Just Add Salt to the Water for Electrolytes?
The short answer here is yes—adding salt to water provides your body with electrolytes. However, if you recall the initial list of electrolytes, sodium replenishment alone won’t fulfill your needs for all of your electrolyte intake.

Ways to Enhance Hydration Naturally for Better Health and Rehydration
As a dietitian, I often encourage a “food first” approach to eating and drinking. What do I mean by this? Instead of turning to supplements, pills, and powders, I encourage you to find ways to get the majority of what you need from natural food and beverages.
There are many foods and beverages that naturally contain electrolytes, salt being one of them. Other common options include bananas, yogurt, milk, coconut water, and fruit juice.
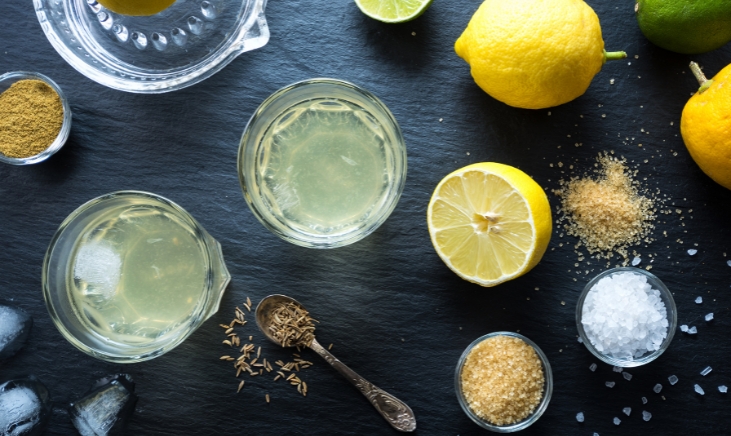
While selecting an electrolyte beverage may seem like an easy option for electrolyte replenishment, I challenge you to at least try making your own to enhance your hydration naturally.
You can make your own electrolyte beverage at home by combining coconut water with your favorite fruit juice and a pinch of any type of salt. This gives you the benefits of the salt, along with additional electrolytes from the coconut water and fruit juice to boost your electrolyte intake.

Summary
Salt is composed of sodium and chloride, two important electrolytes. Some variations also contain trace minerals. However, these differences in composition are not significant enough to alter how they hydrate your body. Try pairing your favorite salt with fruit juice and coconut water for a naturally well-rounded electrolyte boost.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it OK to drink salt water every day? What if I have high blood pressure?
We all need electrolytes daily, including sodium. However, many of our diets provide plenty of sodium, possibly even too much sodium, daily. So, how much salt is too much salt?
In general, experts recommend consuming a maximum of 2300 milligrams of sodium daily, which is equal to about 1 teaspoon of salt for overall health and blood pressure.
If you are an athlete or active individual who is regularly sweating, your sodium needs are higher than this. More specifically, if you are training in hot weather and sweating more than usual, you will need even more sodium. However, your exact needs will vary based on how much you sweat and how salty of a sweater you are.
On the flip side, if you have high blood pressure, you are encouraged to further limit your sodium intake as sodium causes increases in blood pressure.
As with most things in nutrition, it is best to talk with your doctor, dietitian, or other healthcare provider about your specific needs before making decisions about what to do on a daily basis.
Is eating salt the same as drinking electrolytes?
No, eating salt and drinking electrolytes are not the exact same thing. As we discussed above, ingesting salt provides your body with sodium and chloride. Depending on the type of salt, it may also provide you with small amounts of other minerals but nothing substantial.
Drinking electrolytes in the form of sports drinks, oral hydration solutions, electrolyte powders, or electrolyte tablets will provide you with more than just sodium and chloride. However, each electrolyte drink will vary in its composition. Reading the label of what you are consuming will give you the exact details.
What is the best source of electrolytes?
There isn’t necessarily one best source of electrolytes for everyone in every situation.
On one hand, if you take a food first approach, you may say that food sources of electrolytes are the best way to get them. This is valid and can help you continually consume electrolytes to keep your electrolyte levels high.
On another hand, if your electrolyte levels are depleted, you can add electrolytes in the form of an electrolyte beverage as a quick way to replenish and rehydrate when your body really needs it. In this scenario you could use a sports drink, electrolyte power, or electrolyte tablet for a quick, concentrated dose of electrolytes. You could also make a homemade electrolyte drink as we discussed above.
The bottom line is while electrolytes matter, the best source depends on the situation.