Creatine monohydrate (CM) is a popular fitness supplement that enhances muscle mass and strength, improves power, and accelerates recovery. Dozens of creatine products exist on the market. Still, Creapure creatine is often referred to as the gold standard, as it contains 99.9% pure creatine by weight, making it purer and more effective than traditional creatine products.
Quick Look
- Creatine is an amino acid derivative critical for supplying energy to tissues with high energy demands.
- Increasing muscle mass and strength, enhancing anaerobic power, and accelerating recovery are the primary benefits of taking creatine.
- CM is creatine bound to a water molecule and contains about 88% creatine by weight, whereas Creapure is another form of CM containing 99.9% pure creatine by weight.
- Creapure is the superior form of CM due to its greater purity and effectiveness.
Table of Contents
What Is Creatine?
Creatine is an amino acid derivative naturally produced in the body from three amino acids (arginine, glycine, and methionine) and is also widely available in animal proteins.
In the adult human body, creatine is found in the highest concentrations in muscle cells and other metabolically active tissues, where it’s used as an energy substrate in the phosphocreatine (PCr) system. It’s advantageous during intense exercise or power-based activities where energy demands increase significantly, such as weightlifting, powerlifting, or sprints.
While the liver naturally produces about 1-2 grams of creatine per day, supplementing with CM has become a standard practice for athletes, thanks to its ability to boost creatine concentrations in skeletal muscle and support muscle growth and power.
Put simply, the high-energy phosphate bonds in creatine phosphate are broken to release energy to reconstitute adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and supply enough energy for short-duration, explosive work.
How Creatine Works
The primary function of creatine is to supply energy to tissues with high energy demands, such as the brain and muscle cells. This happens through phosphocreatine’s high-energy phosphate bonds that can immediately replenish ATP stores during energy-demanding circumstances.
Here’s how it works.
The phosphagen system consists of two parts:
- ATP store
- Phosphocreatine (PC) or creatine phosphate store
The ATP store in the body is small and provides sufficient energy for about 1-2 seconds of maximal effort. After that, the body must rely on other sources of ATP to supply enough energy to meet the demands. Because muscles can’t obtain ATP from other tissues, they manufacture it using three pieces:
- ADP (adenosine diphosphate)
- Inorganic phosphate (Pi)
- Energy (from other chemical sources) to resynthesize ATP molecules via rephosphorylation of ADP
This is how it works:
ADP + Pi (plus energy) → ATP
One method to increase ATP levels is to break down creatine phosphate—a stored chemical containing a high-energy phosphate bond to release energy. This allows for ATP to be resynthesized from ADP and Pi; creatine phosphate then degrades into creatine + a phosphate ion + energy.
But where does this energy come from? When the phosphate bonds in phosphocreatine are broken, it releases 43.3 kJ (10.3 kcal) per mole—this is significantly higher than breaking the energy bonds in ATP, suggesting that it’s more than enough energy to resynthesize ATP.
However, while the ATP-PCr system can only supply energy to sustain about 5 to 8 seconds of maximal effort, this system is the most rapidly available energy source for explosive and power activities.
So, the theory behind taking exogenous creatine is to boost intramuscular levels of creatine, increasing concentrations of creatine phosphate for ATP production. The more energy you can produce, the harder you can work.
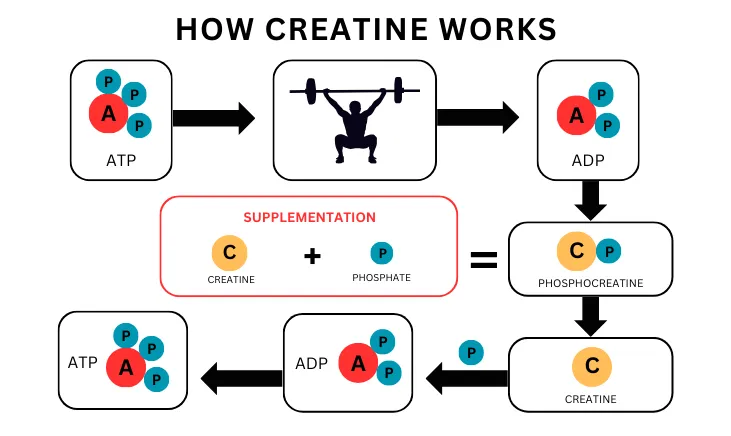
Key takeaway: Creatine is transferred into muscle cells, where it increases phosphocreatine levels. PCr is an essential component of the ATP-PCr system that generates ATP via the breakdown of phosphocreatine stored in muscle cells. This breakdown releases an inorganic phosphate molecule, which combines with ADP to form ATP. The ATP-PCr system is the fastest source of ATP for active muscle tissue.
Health Benefits of Creatine Supplements
Increase Strength and Muscle Mass
Strength and muscle mass are the two primary reasons people take creatine. Because creatine supplementation increases intramuscular creatine stores and ATP availability, it can enhance work capacity, especially during heavy lifting.
Here’s how.
As we said, the ATP-PCr system can only sustain maximal effort for a maximum of about 10 seconds. After this, your body must produce new ATP to match the body’s energy demands. But because heavy lifting requires more ATP per second than your body can produce, exogenous creatine increases your body’s phosphocreatine stores, which go towards producing ATP during high-intensity exercise.
But it doesn’t take months to see a difference.
Studies have shown that a 6-day creatine load (20 g/day) followed by a 2 g/day maintenance dose can drastically increase muscle creatine stores, as shown in the graph below.
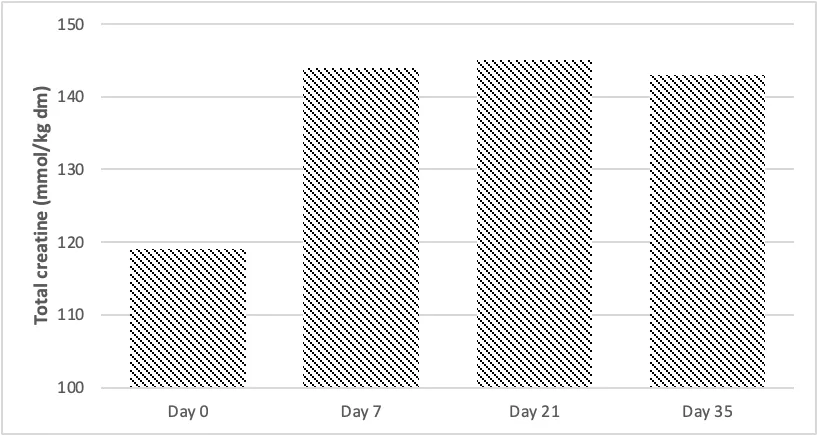
Because muscle creatine stores increase with creatine supplementation, the additional creatine can be used for ATP production, providing extra energy to delay fatigue.
Here is some of the research:
- A 2003 study published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning found that the average increase in muscle strength after creatine supplementation combined with weight training was 8% higher than the average increase in muscle strength for people taking a placebo during resistance training. Creatine supplementation also led to 14% more reps performed at a given load.
- A 2000 study published in Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise looked at the effects of 6 weeks of oral creatine supplementation during a periodized arm flexor strength training program on arm flexor 1RM, upper arm muscle area, and body composition. Results showed that creatine supplementation led to a 15% increase in weight (11 lbs/5 kg) for a 1RM bicep curl. Researchers concluded that creatine supplementation led to greater gains in arm flexor muscular strength, upper arm muscle area, and fat-free mass than strength training alone.
- A 2006 study published in the International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism found that creatine supplementation increased maximum squat and bench press strength but led to a 20% increase in testosterone levels compared with only 5% in the placebo group.
Key takeaway: The primary reason creatine is so effective for muscle growth and strength is its ability to rapidly replenish ATP levels via stored phosphocreatine. With more energy, you can complete more reps, induce more muscle damage, and, ultimately, more muscle growth.
Enhance Anaerobic Power
Anaerobic exercise is any short, fast, high-intensity training that doesn’t require the presence of oxygen. To supply energy anaerobically, the body breaks down intramuscular glucose (or carbs and fat) for energy.
A 2019 study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition looked at the effects of creatine combined with various electrolytes on upper and lower limb anaerobic power and strength. The following metrics were measured for bench press and back squat at pre- and post-test over six weeks of supplementation:
- Maximal strength
- Total concentric work
- Mean rate of force development (mRFD)
- Mean power
- Peak power
- Peak force
Results showed significant increases of 13.4% in back squat 1RM for the group taking the creatine supplement, an increase of 5.9% in bench press maximal strength, and a significant increase in total concentric work and mean power for maximal repetition bench press test at 80% of their 1RM.
A study published in Nutrients found that taking creatine improved anaerobic power in a 30-second all-out cycling sprint test. This suggests that taking creatine could help you sustain high-intensity exercise for longer.
Creatine doses can vary based on how fast you want to saturate creatine stores:
- Loading strategy: 20 g/day for 5-7 days to maximize muscle saturation, followed by 2-5 g/day to maintain muscle levels
- Non-loading strategy: 3-5 g/day daily (it can take up to 28 days to maximize muscle saturation)

Key takeaway: Creatine loading at 20 g/day for up to a week, followed by a maintenance dose of 5 g or less per day, can benefit high-intensity anaerobic activity and may improve exercise performance.
Accelerate Recovery
Creatine’s ability to replenish energy stores between bouts of high-intensity training may help reduce feelings of fatigue and accelerate recovery.
Taking creatine is an effective means to boost intramuscular PCr concentrations by up to 40%. During high-intensity bouts of activity lasting 0–30 seconds, the ATP-PCr system is the primary driver of energy production, so enhancing substrate availability is one way to maximize energy output.
Research suggests that enhanced physical performance results from two things:
- Higher initial intramuscular PCr concentration pre-exercise
- Enhanced PCr resynthesis during recovery periods
As such, maximizing creatine stores and PCr availability before training can increase ATP availability throughout the successive bouts of exercise, which can help mitigate decreases in power output and fatigue.
It’s also important to note that exercises characterized by a high force output rely more heavily on type II muscle fibers, which have a higher PCr content than the more oxidative type I fibers; type II fibers are favored during near or maximal effort exercises using a high degree of force output.
Key takeaway: Supplementing with creatine can enhance PCr resynthesis during recovery periods to maintain force production and power output.
What Is Creapure Creatine?
While there are several forms of creatine, CM is the most popular and well-researched.
One specific brand of CM is Creapure—it’s manufactured using water as a solvent by German company AlzChem Trostberg GmbH. Although still a form of creatine, Creapure is one of the purest products on the market, backed by abundant research and proven safe and effective. The product contains 99.9% pure CM with no contaminants.
Creapure is vegan and exclusively manufactured by chemical synthesis. It is also IFS FOOD certified, a quality standard recognized by the “Global Food Safety Initiative.”
You can also find other forms of Creapure:
- Creapure® AH: CM typically contains about 88% creatine, while anhydrous contains 100%.
- Creapure® Citrate: Creapure Citrate contains creatine and citrate in a 3:1 ratio. While pure creatine is tasteless, adding citrate gives it a lemon flavor and improves solubility.
- Creapure® pH 10: Contains creatine mixed with a sodium carbonate buffer to form an alkaline solution with a pH of about 10.
- Creapure® Gluco: Creapure Gluco is a chewable tablet containing Creapure and a small amount of dextrose. Each tablet contains one gram of CM that can be taken without water; these are especially helpful during activities.
Creatine Monohydrate vs Creapure
The process of producing creatine is important for the purity and efficacy of the product. Poor manufacturing practices and handling of the raw material can lead to more impurities and, therefore, a less effective product.
However, the technical process of creating Creapure CM makes it so different from other forms of creatine—fewer impurities, thanks to better manufacturing practices, mean a purer product.
CM, for example, contains about 88% pure creatine by weight, whereas the creatine content of other forms can be as little as 40%; how much creatine they contain depends on the product. Creapure, however, contains 99.9% pure creatine, making it one of the purest and most effective creatine supplements available.
What Is Micronized Creatine?
Micronized creatine is a form that goes through additional processing to shrink the particle side by about 20x. Smaller particles improve solubility and mixability and make creatine more readily and easily absorbed by the body. Because bioavailability is better, micronized creatine monohydrate is often thought to be more effective.
Due to better efficacy, micronized creatine typically doesn’t have the same side effects as other forms of creatine, such as GI discomfort.
Creapure vs Micronized Creatine
While Creapure is one of the most popular forms of creatine and the gold standard for studies, micronized creatine is becoming increasingly popular for two reasons:
- Easier for the body to absorb and use
- It doesn’t cause the same GI issues (stomach upset and water retention) that CM does
Because of this, micronized creatine offers a more effective and comfortable choice for athletes looking for the benefits of creatine without the side effects.
What Makes Creapure Better?
Purity
As mentioned, CM contains about 88% pure creatine by weight, whereas Creapure contains 99.9%, offering a significantly purer and more effective product.
Manufacturing conditions and handling raw materials are critical factors in determining the quality of CM. Inferior raw materials or too-rapid water reduction during recrystallization can lead to larger amounts of impurities (creatinine, dicyandiamide, and dihydrotriazine) in the final product.
Additionally, Creapure has been specially tested for the presence of these impurities using high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) to ensure it is as pure as possible. Due to its patented system for synthesizing creatine, Creapure is known for its quality and purity.
Increased Muscle Mass
A purer product offers more efficacy in terms of gaining muscle mass. Because Creapure contains 99.9% pure creatine, it’s more effective at increasing phosphocreatine levels to replenish your ATP reserves, giving you greater energy availability and a greater capacity to work. SImply put, Creapure boosts muscle growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Creapure the best creatine?
Creapure is often considered the gold standard for scientific studies due to its higher percentage of pure creatine. However, some people may find other forms of creatine more effective in achieving their fitness goals.
Is Creapure better than creatine monohydrate?
Creapure is a form of C that contains 99.9% pure creatine by weight. A higher percentage of creatine can saturate muscle creatine stores faster and increase phosphocreatine levels to replenish ATP stores.
Why is Creapure so expensive?
While there are several advantages to choosing Creapure over other creatine products, price can be a sticking point. CM products are typically more affordable, but Creapure is expensive due to the additional processes it goes through to enhance purity, which increases the price.